IT security audit: Let's learn more
You’ve pulled together the reports. You’ve checked the boxes. But now comes the big question: Did you really understand what all that meant?
An IT security audit can feel like a grand ceremony with multiple teams, thick binders, checklists galore. But if it ends there, you’ve missed the point. An audit isn’t a trophy; it’s a tool. One that, when wielded right, gives you clarity on your risk, your controls, and your next moves.
If you’re ready to move beyond the surface and into the meat of what an audit can truly deliver, this edition of All Things AppSec is for you.
What is an IT security audit (really)?
An audit is not just a “find-and-fix” exercise. At its core, an IT security audit is a comprehensive and periodic evaluation of your policies, infrastructure, processes and controls.
How it shows up:
Reviewing how your firewall rules are set up
Validating user access policies (who can do what, and is that still valid?)
Checking patching and configurations across your systems
Confirming data is classified, encrypted, handled, and disposed properly
Making sure security is baked into everything from dev workflows to disaster recovery
When done right, an audit gives you a map: where you are, where you should be, and how far you have to go.
Why regular audits are non-negotiable
It’s easy to treat audits like annual chores. But what do you actually get when you do them well?
Proactive risk reduction – The best time to find a gap is before it’s exploited.
Regulatory alignment – Whether you’re under GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS or ISO-27001, audits help you demonstrate compliance and avoid fines.
Business resilience – Audits evaluate your incident response, backup, disaster recovery. So, when something goes wrong, you don’t lose everything.
Trust & reputation – Showing partners, customers and stakeholders you take security seriously matters now more than ever.
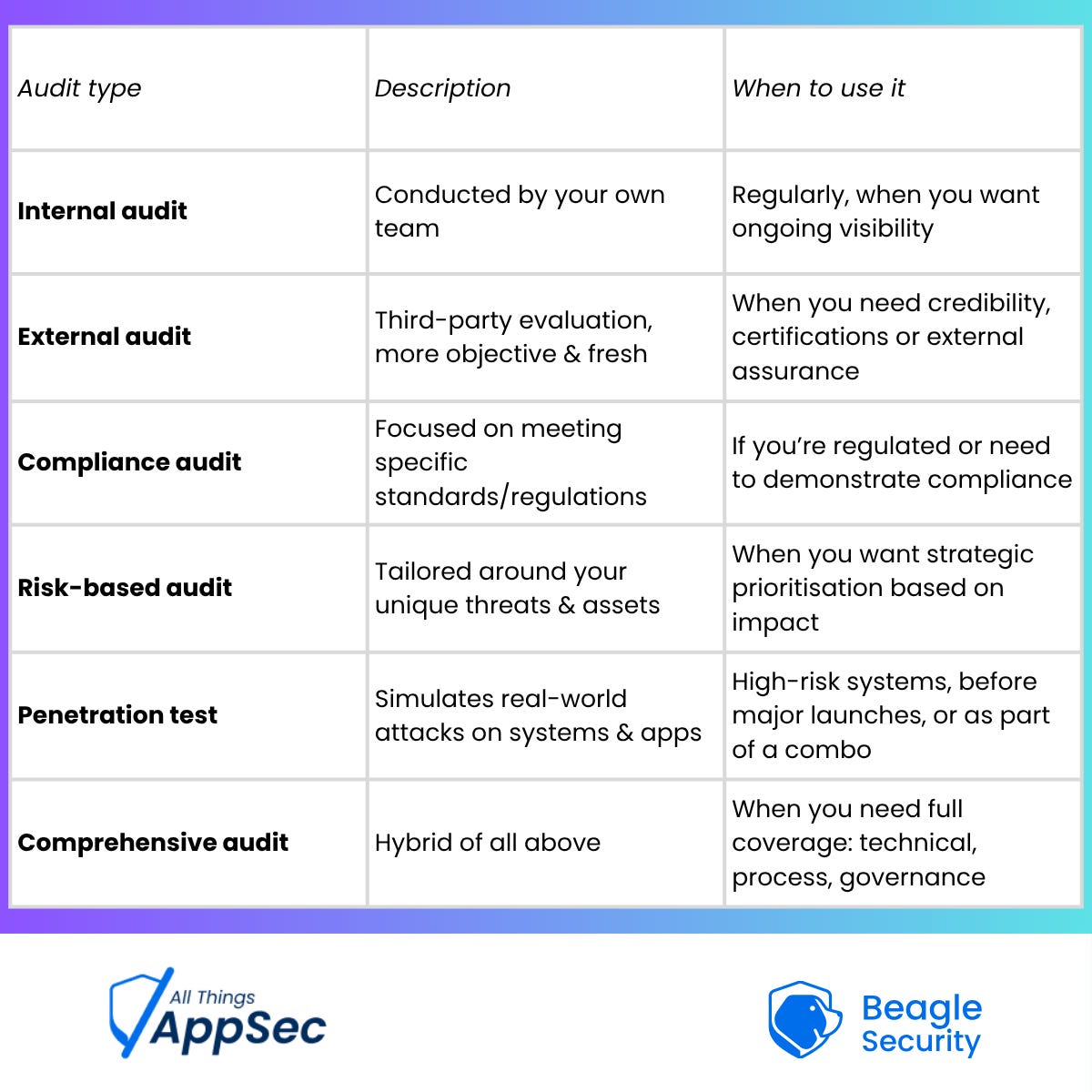
Types of audits: Picking what fits you
Not all audits are created equal. Here are the major types you’d want to be familiar with:
Choosing the right type (or combination) matters because it helps you spend wisely and target what matters most.
When and how often should you audit?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but guidelines help set expectations.
At least annually for full assessments.
Continuous monitoring and interim reviews for high-risk systems or changing environments.
Trigger-based audits should happen after major events: new system deployments, major architecture changes, mergers/acquisitions, or after a breach.
More frequent audits may be required in sectors like healthcare, finance or government.
Your goal: align frequency with your risk profile and environment changes.
Best practices for smarter audits
A checklist helps, but the mindset behind it counts more. Here’s how to elevate your audit game:
Define clear objectives & scope – Before you start, know what you’re auditing and why.
Follow recognised frameworks – Use NIST, ISO 27001, CIS Controls as your foundation.
Build continuous visibility – Audits shouldn’t be once-a-year surprises. Use monitoring, automation, dashboards.
Stay ahead of threats – Threat actors evolve; your audit methods should too. Training, red-teaming, fresh expertise matter.
Collaborate across teams – Security isn’t just an IT problem. Get business, legal, operations involved.
Report with clarity & priority – Findings should have business impact context, clear next actions, and a prioritization strategy.
Test incident response via exercises – Table-top drills help ensure procedures work under pressure.
Focus on risk, not just vulnerabilities – Identify what matters most to your organisation and protect accordingly.
IT security audit checklist – Key areas
Here are high-value controls to include in your audit:
Governance & policy: Security strategy, training, documentation align with business goals.
Risk management: Risk identification, treatment plans, vendor assessments.
Access control & identity management: MFA, role separation, session controls.
Network security: Architecture, segmentation, remote access protections.
Applications & systems: Patch management, secure development practices, vulnerability management.
Data protection: Encryption in transit and at rest, backups, data retention.
Physical security: Facility access controls, media disposal, environmental safeguards.
Incident management: Response plans, escalation procedures, lessons-learned integration.
Compliance & third-party risk: Regulations, contractual requirements, vendor security practices.
Use this as your starting toolkit. Adapt and expand it based on what’s unique to your business.
Why this matters for AppSec teams
Your application security efforts (pentests, code reviews, CI/CD scanning) live inside this bigger ecosystem. A robust audit helps you:
See how your app fits into bigger infrastructure and controls
Prioritize tests based on real risk (not just CVSS)
Align development, operations, and security around the same goals
Demonstrate value and security maturity to stakeholders
When your AppSec program aligns with audit insights, you move from reactive to strategic.
Final thoughts
Audits should feel uncomfortable. If you walk away nodding and don’t question anything, you’re doing it wrong. The best audits surface unexpected truths, challenge assumptions, and push real action.
So, set goals. Define scope. Get visibility. Use this checklist. And treat your audit as more than a one-time event.
After all, you’re not just checking boxes. You’re protecting real assets, real users, and real trust.